The evolution of diagnostic imaging has reached a pivotal moment with a technology that fundamentally redefines our ability to see inside the human body with breathtaking clarity and unprecedented safety. The introduction of photon-counting CT technology represents a significant advancement, moving beyond incremental improvements to establish a new paradigm. This review will explore the evolution of this technology, its key features, clinical performance, and the impact it is having on patient care and diagnostics. The purpose of this review is to provide a thorough understanding of the technology, its current capabilities, and its potential future development as a new standard in medical imaging.
Fundamentals of Photon-Counting CT Technology
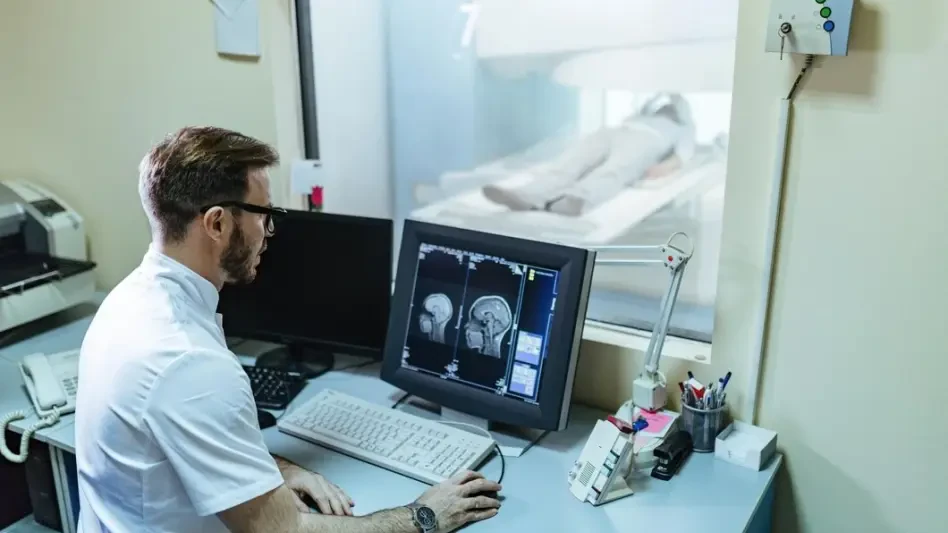
At its core, photon-counting CT technology represents a departure from the conventional energy-integrating detectors that have been the standard for decades. Traditional CT scanners measure the total energy of all X-ray photons that strike the detector, essentially averaging the signal. This process can introduce electronic noise and lose valuable information about the different energy levels of the photons. In contrast, photon-counting detectors directly register each individual X-ray photon and measure its specific energy level, creating a much cleaner and more data-rich signal.
This next-generation scanner has emerged in a healthcare landscape increasingly focused on precision medicine and patient-centric care. By providing more detailed anatomical and functional information, it empowers clinicians to make more personalized diagnostic and treatment decisions. This shift from a one-size-fits-all approach to tailored medical intervention is where photon-counting CT finds its greatest relevance, offering a tool that matches the growing demand for higher precision and greater patient safety.
Key Features and Technological Advantages
Direct Photon Detection and Spectral Imaging
The primary technological leap of photon-counting CT is its ability to directly detect and count individual X-ray photons while simultaneously measuring their energy levels. This direct conversion process eliminates intermediate steps that create electronic noise in conventional systems, resulting in a significantly improved signal-to-noise ratio. The outcome is an inherently cleaner, more robust image dataset from which to make a diagnosis.
Furthermore, by sorting photons into multiple energy bins, the technology enables intrinsic spectral imaging. This capability allows for material differentiation, making it possible to distinguish between different types of tissue, such as calcium, iodine, and soft tissue, with far greater accuracy. This is a significant advance over conventional dual-energy CT, offering more detailed compositional information from a single scan and opening new diagnostic possibilities.
Unprecedented Spatial Resolution and Image Quality
The direct detection mechanism translates into a remarkable improvement in spatial resolution, producing ultra-high-resolution images with exceptional sharpness and detail. Because the detector elements can be made much smaller without the signal degradation seen in conventional systems, the scanner can visualize anatomical structures that were previously beyond the limits of CT imaging.
This leap in image quality has profound clinical significance. It enables clinicians to identify subtle tissue variations, visualize micro-lesions, and assess intricate vascular and organ structures with previously unattainable accuracy. This ability to see finer details boosts diagnostic confidence and can lead to earlier and more precise diagnoses, fundamentally changing how conditions are managed.
Enhanced Patient Safety Through Dose Reduction
One of the most critical benefits for patients is a significant reduction in radiation exposure. The high efficiency of photon-counting detectors means that high-quality images can be acquired using a lower radiation dose compared to conventional CT scanners. The system’s ability to eliminate electronic noise and make better use of the X-ray spectrum contributes directly to this dose efficiency.
This advancement makes CT scanning safer for all patients but is particularly impactful for sensitive groups. Children, older adults, and individuals requiring frequent follow-up examinations for chronic conditions can now undergo necessary imaging with minimized cumulative radiation exposure. This focus on patient safety without compromising diagnostic quality is a cornerstone of modern, patient-centric healthcare.
Latest Developments and Global Adoption Trends
Recent developments in the field are highlighted by the strategic partnership between Sunway Medical Centre and Siemens Healthineers, which brought Malaysia its first photon-counting CT scanner. This milestone serves as a powerful case study for the emerging trend of global adoption, establishing a new national benchmark in diagnostic imaging and signaling a shift toward this advanced technology in leading medical institutions worldwide.
The collaboration underscores a consensus viewpoint among healthcare providers and technology developers that photon-counting CT is ready for mainstream clinical use. As more hospitals invest in this technology, it is expected to accelerate a global move toward more precise, safer, and more informative diagnostics. This trend is driven by a shared commitment to delivering world-class care through technological innovation.
Real-World Clinical Applications and Impact
Advancements in Cardiology and Neurology
In cardiology, the technology’s high resolution and spectral capabilities allow for the precise visualization of coronary arteries, even in challenging cases, helping to diagnose stenosis and characterize plaque with greater confidence. Similarly, in neurology, the ability to clearly image cerebral vasculature is invaluable for identifying aneurysms, strokes, and other neurological conditions, enabling faster and more accurate clinical decisions.
New Frontiers in Oncology and Pulmonology
For oncology and pulmonology, the enhanced image detail is transformative. It facilitates the early detection and characterization of small tumors and subtle lung pathologies that might be missed on conventional scans. This supports more precise treatment planning and monitoring in cancer care and the management of respiratory diseases, directly impacting patient outcomes.
Specialized Applications for Sensitive Patient Groups
The low-dose capabilities of photon-counting CT are paramount in fields where radiation exposure is a primary concern. In pediatrics, it provides a much safer imaging option for children, who are more sensitive to radiation. It is also highly beneficial for musculoskeletal assessments and for patients undergoing multiple follow-up scans for chronic disease management, as it minimizes the cumulative radiation dose over a patient’s lifetime.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
Despite its clear advantages, the widespread adoption of photon-counting CT faces several challenges. The high initial investment cost is a significant barrier for many healthcare institutions, limiting its availability outside of major medical centers. The advanced nature of the technology also requires specialized training for radiologists and technologists to fully leverage its capabilities and interpret the data-rich images it produces.
Furthermore, integrating this next-generation technology into existing hospital workflows and data management systems presents logistical complexities. The massive datasets generated by spectral imaging require robust IT infrastructure for storage and analysis. Ongoing development efforts are focused on mitigating these barriers through cost reduction, streamlined training programs, and improved software integration to facilitate a smoother transition.
Future Outlook and Technological Trajectory
The trajectory of photon-counting CT technology points toward an even more integrated role in medicine. Future breakthroughs are expected to expand its applications into functional imaging and molecular diagnostics, allowing clinicians to not only see anatomy but also to visualize biological processes at the cellular level. This could revolutionize how diseases are understood and treated.
In the long term, this technology is poised to transform diagnostic pathways and establish a new gold standard in precision medicine. As it becomes more accessible, its ability to provide comprehensive diagnostic information from a single, low-dose scan will likely reduce the need for multiple imaging tests, improving efficiency and enhancing the patient experience.
Conclusion A New Frontier in Diagnostic Certainty
The consensus from clinicians, technology developers, and healthcare providers is clear: photon-counting CT is a transformative tool. It fundamentally enhances diagnostic capabilities by delivering superior image quality and quantitative spectral information simultaneously. This review confirms that the technology is no longer an experimental concept but a clinical reality that is actively improving patient care.
Ultimately, this innovation represents a new frontier in the quest for diagnostic certainty. By boosting clinician confidence, significantly enhancing patient safety through dose reduction, and paving the way for more personalized medicine, photon-counting CT is ushering in a new era of precision diagnostics. Its impact is already being felt, and its potential to reshape medical imaging is only just beginning to be realized.